Viscosity power law
Home » Query » Viscosity power lawYour Viscosity power law images are available in this site. Viscosity power law are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Viscosity power law files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for viscosity power law images information related to the viscosity power law topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
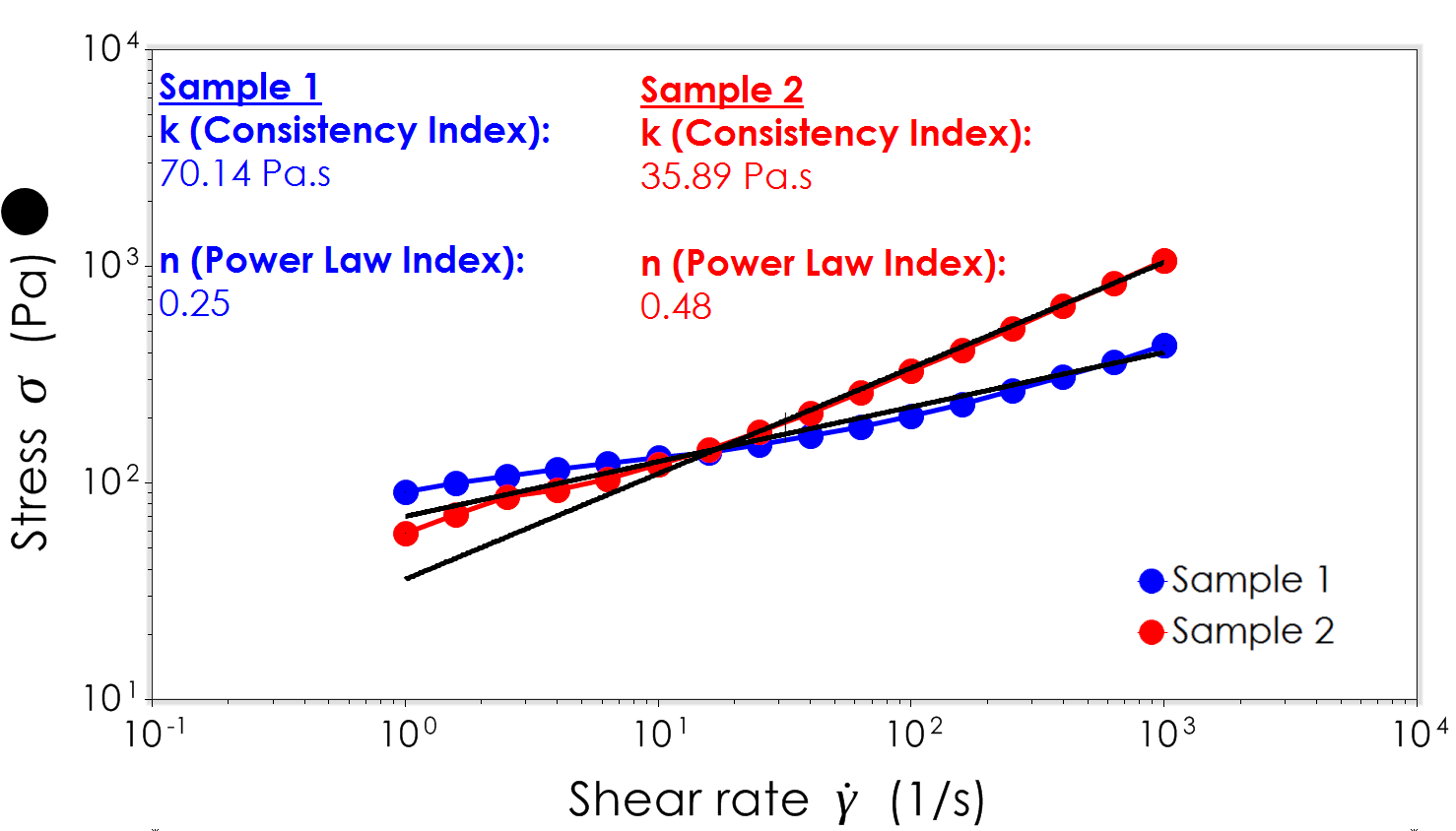
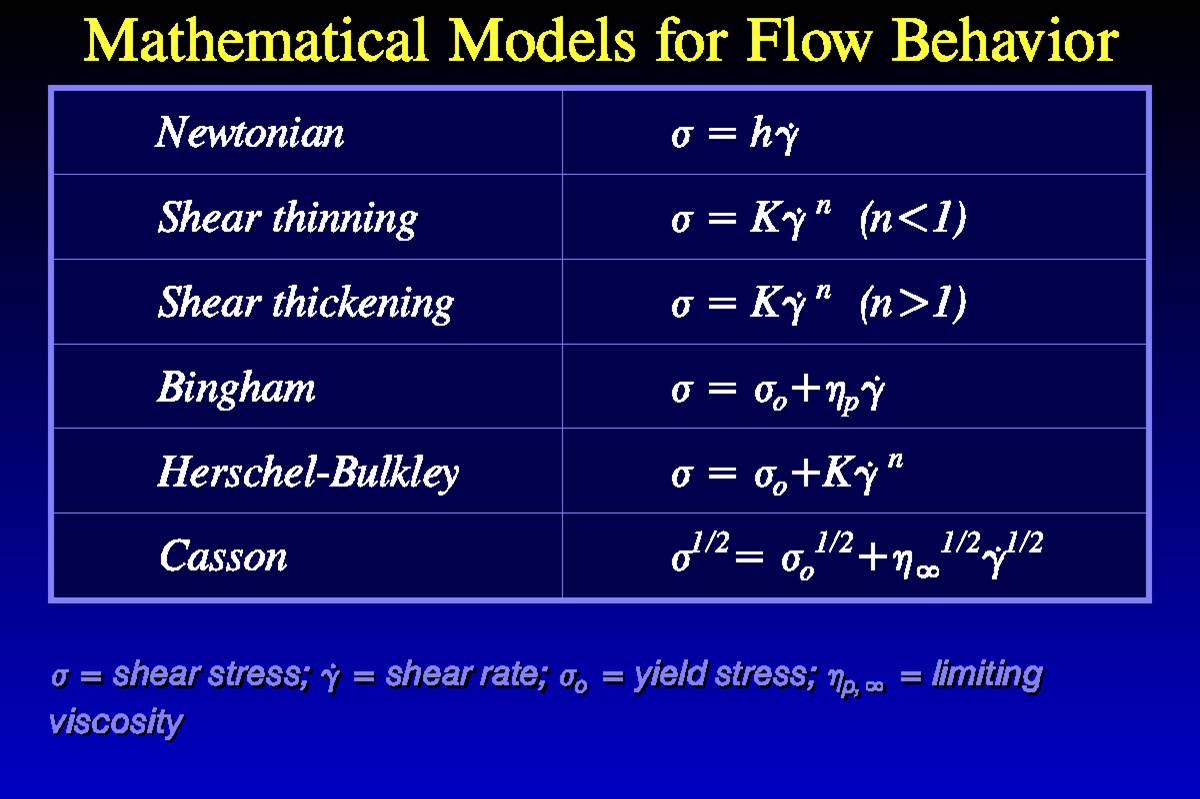
Viscosity Power Law. Viscosity is a function of shear rate. The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries. Where is the viscosity in kgm-s is the static temperature in K is a reference value in K is a reference value in kgm-s. η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau region.
 Non Newtonian Models Materials Simscale From simscale.com
Non Newtonian Models Materials Simscale From simscale.com
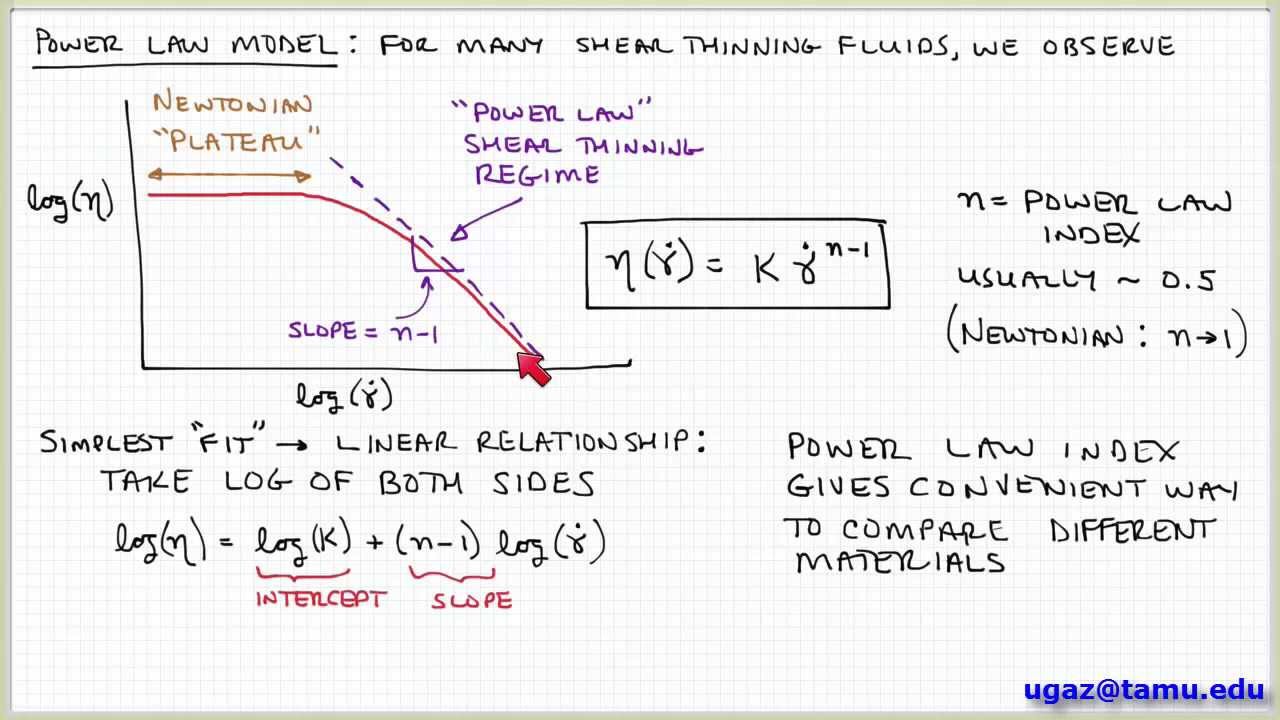
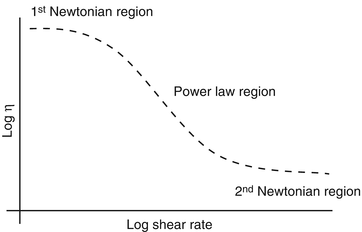
For example syrup has a higher viscosity than water. The Power law behavior dominates at higher shear rates where the viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate with a negative slope of n 1. Power Law Index n The power law index measures the degree of the non-Newtonian behavior. This value will be entered as the variable C in the expression to calculate the viscosity. For a power - law constitutive relation μ Kγn - 1 Equation 9 can be inverted to obtain an. Power law model is applicable for time independent non-Newtonian fluids and can be written as τ K γ n.
The power-law viscosity law can also be written as.
For example syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Rheology-Processing Chapter 2 10. Polymers have a consistency index m and a power-law coefficient n that describe its general viscosity behavior with respect to changing temperature T and shear rate Ÿ. Equation 313 is called the Newtons law of viscosity and states that the shear stress between adjacent fluid layers is proportional to the negative value of the velocity gradient between the two layers. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. Kinematic Viscosity of Water vs.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Where τ is shear stress γ is shear rate K is called flow consistency index and n is called flow behavior index. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. I was able to tune the consistency index k power-law index n and maximum and minimum viscosity limit. Newtons Law of Viscosity Newtons law of viscosity states that. The n parameter is known as the Power-law index.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Kinematic Viscosity of Water vs. Note that consistency indexmis equal to viscosity ηat On a log-log paper ηvs is a straight line and the slope is equal ton-1. The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids it corresponds to the informal concept of thickness. The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries.
Source:
Equation 313 is called the Newtons law of viscosity and states that the shear stress between adjacent fluid layers is proportional to the negative value of the velocity gradient between the two layers. The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries. This value will be entered as the variable C in the expression to calculate the viscosity. η min η η max. The power-law model also describes the flow behavior of many polymer solutions although the relationship between the friction factor and the Reynolds number differs from that required to describe the behavior of concentrated slurries.
 Source: ptonline.com
Source: ptonline.com
In literature most experimental studies on drilling fluids observed that the drilling fluid rheological curves rheogram conformed best to that of YPL. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. The model is nothing more than the Newtonian model with an added exponent on the shear rate term. Moorthy2 1 Department of Mathematics K. The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate.
 Source: azom.com
Source: azom.com
The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998. Viscosity can be conceptualized as quantifying the internal frictional force that arises between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. Newtons Law of Viscosity Newtons law of viscosity states that. For air at moderate temperatures and pressures and. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step.
 Source: rheologylab.com
Source: rheologylab.com
For a power-law constitutive relation μ K γ n-1 Equation 9 can be inverted to obtain an effective shear rate γ eff. To calculate the viscosity power-law model is a simple consti-tutive model that shows good description of fluid behavior across the range of shear rates to which the coefficients were fitted while Casson model also considers yield stress in term of blood viscosity. Moorthy2 1 Department of Mathematics K. Power Law Index n The power law index measures the degree of the non-Newtonian behavior. Log log m n 1 log.
 Source: simscale.com
Source: simscale.com
The power-law viscosity law can also be written as. Kinematic Viscosity of Water vs. The model is nothing more than the Newtonian model with an added exponent on the shear rate term. I need to provide high viscosity of the input fluid and observe the shear-thinning. Viscosity can be conceptualized as quantifying the internal frictional force that arises between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion.
Source: researchgate.net
Kinematic Viscosity of Water vs. This property is only applicable to steady and unsteady fluid flow analyses. Note that there exists a. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more.
 Source: azom.com
Source: azom.com
Temp Temp oC Viscosity m2s 0 179 x 10-3 10 131 x 10-3 MPDFFOLect_3 20 100 x 10-3 30 797x 10–4 40 65 x 10-4. Effects of Variable Viscosity on Power-Law Fluids over a Permeable Moving Surface with Slip Velocity in the Presence of Heat Generation and Suction T. Power law model is applicable for time independent non-Newtonian fluids and can be written as τ K γ n. This property is only applicable to steady and unsteady fluid flow analyses. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds.

In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. K is often known as the consistency coefficient. η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau region. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds. In literature most experimental studies on drilling fluids observed that the drilling fluid rheological curves rheogram conformed best to that of YPL.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries. The power-law relation gives. Log log m n 1 log. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. Viscosity is a function of shear rate.
 Source: rheologylab.com
Source: rheologylab.com
Rheology-Processing Chapter 2 10. Fluids that obey Newtons law of viscosity are called Newtonian fluids. The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. Viscosity is a function of shear rate.
 Source: iq.usp.br
Source: iq.usp.br
Viscosity can be conceptualized as quantifying the internal frictional force that arises between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. The consistency index is primarily the relationship between the. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more. This property is only applicable to steady and unsteady fluid flow analyses. The power law model is commonly used to describe the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Where is the viscosity in kgm-s is the static temperature in K is a reference value in K is a reference value in kgm-s. The power-law model also describes the flow behavior of many polymer solutions although the relationship between the friction factor and the Reynolds number differs from that required to describe the behavior of concentrated slurries. Power law model is applicable for time independent non-Newtonian fluids and can be written as τ K γ n. Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields. The power-law viscosity law can also be written as.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The power-law model also describes the flow behavior of many polymer solutions although the relationship between the friction factor and the Reynolds number differs from that required to describe the behavior of concentrated slurries. The Power Law model sometimes known as the Ostwald model is an easy-to-use model that is ideal for shear-thinning relatively mobile fluids such as weak gels and low-viscosity dispersions. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0. Newtons Law of Viscosity Newtons law of viscosity states that. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more.
 Source: polymerdatabase.com
Source: polymerdatabase.com
The power-law relation gives. The n parameter is known as the Power-law index. For a power-law constitutive relation μ K γ n-1 Equation 9 can be inverted to obtain an effective shear rate γ eff. Note that there exists a. For liquids it corresponds to the informal concept of thickness.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
For example syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Where τ is shear stress γ is shear rate K is called flow consistency index and n is called flow behavior index. To calculate the viscosity power-law model is a simple consti-tutive model that shows good description of fluid behavior across the range of shear rates to which the coefficients were fitted while Casson model also considers yield stress in term of blood viscosity. The power-law relation gives. The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Equation 313 is called the Newtons law of viscosity and states that the shear stress between adjacent fluid layers is proportional to the negative value of the velocity gradient between the two layers. The Power Law model sometimes known as the Ostwald model is an easy-to-use model that is ideal for shear-thinning relatively mobile fluids such as weak gels and low-viscosity dispersions. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. This power-law viscosity corresponds to the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid which would have given the same pressure drop ΔpL along a capillary. Rangasamy College of Technology Tiruchengode-637 215 TN India.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title viscosity power law by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.