Power law viscosity
Home » Query » Power law viscosityYour Power law viscosity images are available in this site. Power law viscosity are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Power law viscosity files here. Get all free vectors.
If you’re looking for power law viscosity images information linked to the power law viscosity keyword, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
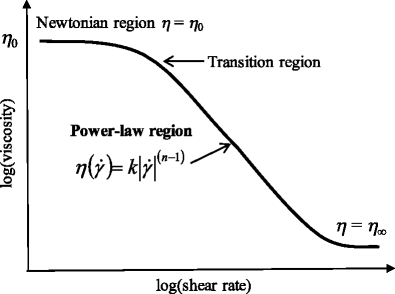
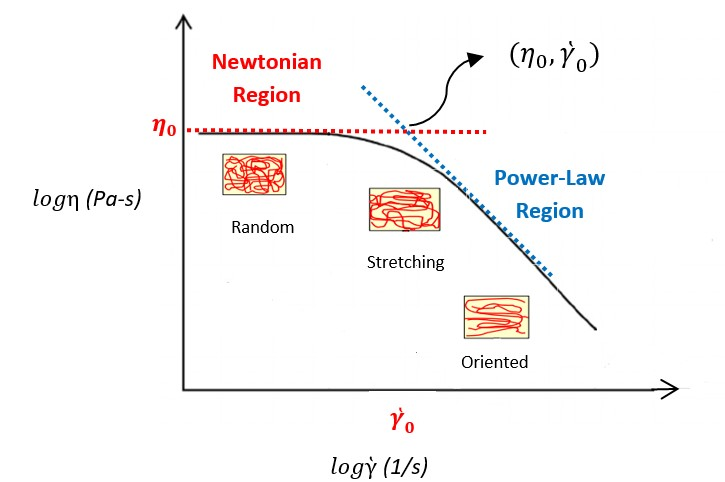
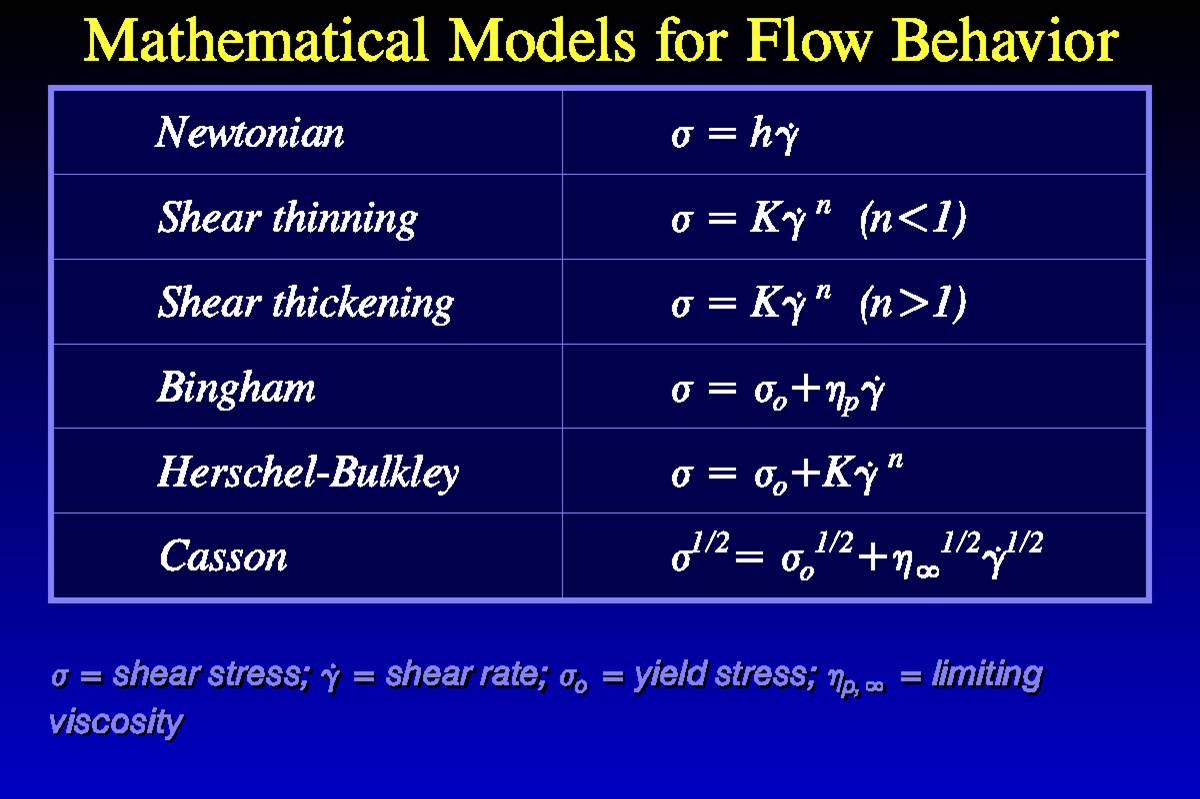
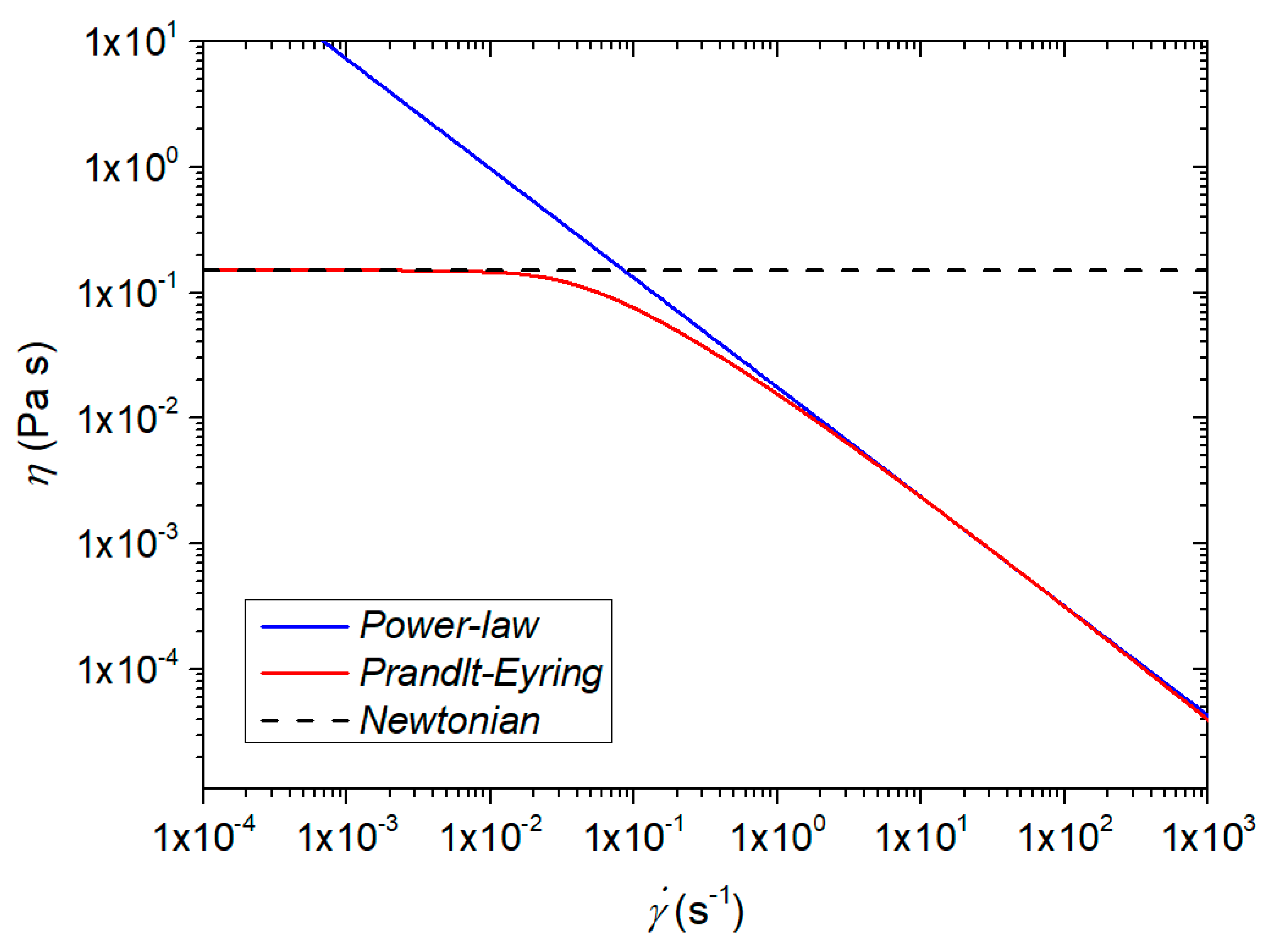
Power Law Viscosity. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0. K is often known as the consistency coefficient. η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau region. The Power Law model sometimes known as the Ostwald model is an easy-to-use model that is ideal for shear-thinning relatively mobile fluids such as weak gels and low-viscosity dispersions.
 Power Law Fluid Graph Demonstration Youtube From youtube.com
Power Law Fluid Graph Demonstration Youtube From youtube.com
Hdgdt m dgdt n-1 The n-1 power is a direct consequence of the first term in the CEF equation having a power of 1 for dgdt. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0. M is the consistency and n is the power-law index. Uy is the shear rate or the velocity gradient perpendicular to the plane of shear SI unit s1 and. η min η η max. K is often known as the consistency coefficient.
Fitting to the power law model is appropriate where the measured data is entirely within the shear-thinning.
Power Law Index n The power law index measures the degree of the non-Newtonian behavior. N is the flow behaviour index dimensionless. Note that there exists a. If a sphere is dropped into a fluid the viscosity can be determined using the following formula. Where ρ is the density difference between fluid and sphere tested a is the. The Power law behavior dominates at higher shear rates where the viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate with a negative slope of n 1.

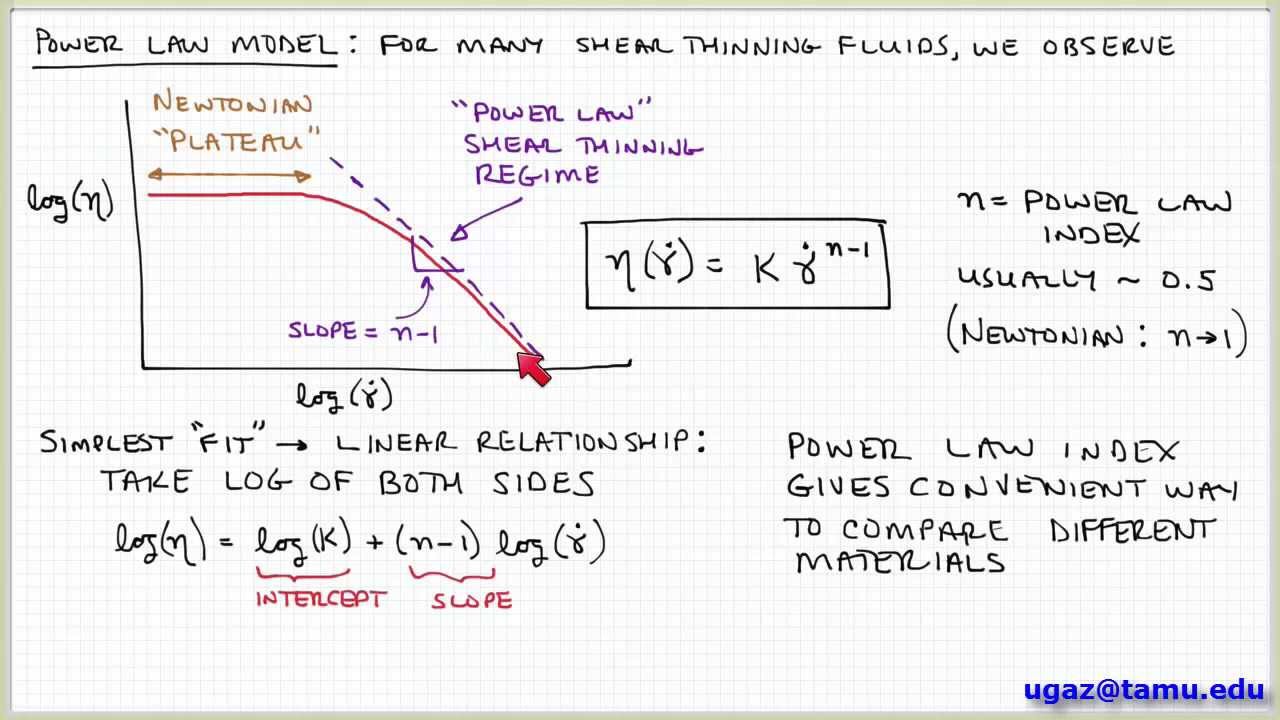
In statistics a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity independent of the initial size of those quantities. Represents an apparent or effective viscosity as a. The viscosity is expressed as η k γ n - 1. Where is the viscosity in kgm-s is the static temperature in K is a reference value in K is a reference value in kgm-s. An alternative interpretation can be given to 313 by noting from.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
24 Equation 313 is called the Newtons law of viscosity and states that the shear stress between adjacent fluid layers is proportional to the negative value of the velocity gradient between the two layers. Note that there exists a. Uy is the shear rate or the velocity gradient perpendicular to the plane of shear SI unit s1 and. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. This value will be entered as the variable C in the expression to calculate the viscosity.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The power-law model also describes the flow behavior of many polymer solutions although the relationship between the friction factor and the Reynolds number differs from that required to describe the behavior of concentrated slurries. If a sphere is dropped into a fluid the viscosity can be determined using the following formula. Hdgdt m dgdt n-1 The n-1 power is a direct consequence of the first term in the CEF equation having a power of 1 for dgdt. For a Newtonian fluid n 1 and m is the viscosity. Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Fitting to the power law model is appropriate where the measured data is entirely within the shear-thinning. For instance considering the area of a square in terms of the length of its side if the length is doubled the area is multiplied by a factor of four. Hdgdt m dgdt n-1 The n-1 power is a direct consequence of the first term in the CEF equation having a power of 1 for dgdt. N is the flow behaviour index dimensionless. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0.
 Source: rheologylab.com
Source: rheologylab.com
The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998. Rheology-Processing Chapter 2 10. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0. Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
For air at moderate temperatures and pressures and. N is the flow behaviour index dimensionless. Where ρ is the density difference between fluid and sphere tested a is the. This power-law viscosity corresponds to the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid which would have given the same pressure drop ΔpL along a capillary. Note that consistency indexmis equal to viscosity ηat On a log-log paper ηvs is a straight line and the slope is equal ton-1.

The Power law behavior dominates at higher shear rates where the viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate with a negative slope of n 1. The Power Law model sometimes known as the Ostwald model is an easy-to-use model that is ideal for shear-thinning relatively mobile fluids such as weak gels and low-viscosity dispersions. This power-law viscosity corresponds to the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid which would have given the same pressure drop ΔpL along a capillary. The Power law model can be used to describe any material that shows power law behaviour. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
If a sphere is dropped into a fluid the viscosity can be determined using the following formula. Uy is the shear rate or the velocity gradient perpendicular to the plane of shear SI unit s1 and. The power-law model provides an alternative to the Bingham plastic model for concentrated non-settling slurries. A power law index n1 denotes that the sample is shear thickening. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Note that consistency indexmis equal to viscosity ηat On a log-log paper ηvs is a straight line and the slope is equal ton-1. Viscosity is measured in terms of a ratio of shearing stress to the velocity gradient in a fluid. A power-law fluid or the Ostwald de Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid time independent Non-Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by n is the flow behavior index dimensionless. 24 Equation 313 is called the Newtons law of viscosity and states that the shear stress between adjacent fluid layers is proportional to the negative value of the velocity gradient between the two layers. A high power law index represents a fluid with a more.
 Source: azom.com
Source: azom.com
Where ρ is the density difference between fluid and sphere tested a is the. M is the consistency and n is the power-law index. K is the flow consistency index SI units Pasn. A Power-law fluid or the Ostwaldde Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by. Viscosity is measured in terms of a ratio of shearing stress to the velocity gradient in a fluid.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Power Law Index n The power law index measures the degree of the non-Newtonian behavior. The Power Law model sometimes known as the Ostwald model is an easy-to-use model that is ideal for shear-thinning relatively mobile fluids such as weak gels and low-viscosity dispersions. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds. The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998. A power-law fluid or the Ostwald de Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid time independent Non-Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by n is the flow behavior index dimensionless.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
If a sphere is dropped into a fluid the viscosity can be determined using the following formula. Newtons Law of Viscosity Newtons law of viscosity states that Shear stress is directly proportional to velocity gradient du τα du τ µ MPDFFOLect_3 µ Viscosity of the fluid Unit of µ Kgms Poise Pas 1 Poise 1gcm. The Power law behavior dominates at higher shear rates where the viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate with a negative slope of n 1. The Power law fluid model is a type of generalized model. The consistency index is primarily the relationship between the.

Fitting to the power law model is appropriate where the measured data is entirely within the shear-thinning. After this the viscosity starts to reduce at a critical shear rate y 0. The power-law viscosity law can also be written as. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds. The relation is given as.
 Source: simscale.com
Source: simscale.com
If a sphere is dropped into a fluid the viscosity can be determined using the following formula. The consistency index is primarily the relationship between the. N. A Power-law fluid or the Ostwaldde Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by. In literature most experimental studies on drilling fluids observed that the drilling fluid rheological curves rheogram conformed best to that of YPL.
 Source: iq.usp.br
Source: iq.usp.br
K is often known as the consistency coefficient. One quantity varies as a power of another. Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields. The power law model is commonly used to describe the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids. In these analyses the viscosity will be calculated based on the shear rate at each step.
 Source: handwiki.org
Source: handwiki.org
K is the flow consistency index SI units Pasn. For a power-law constitutive relation μ K γ n - 1 Equation 9 can be inverted to obtain an effective shear rate γ eff. It gives a basic relation for viscosity nu and the strain rate dotgamma. One quantity varies as a power of another. This value will be entered as the variable C in the expression to calculate the viscosity.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The Power law fluid model is a type of generalized model. The power law model is commonly used to describe the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids. A Power-law fluid or the Ostwaldde Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by. The model is nothing more than the Newtonian model with an added exponent on the shear rate term. η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau region.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Represents an apparent or effective viscosity as a. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. An alternative interpretation can be given to 313 by noting from. The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998. A Power-law fluid or the Ostwaldde Waele relationship is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid for which the shear stress τ is given by.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title power law viscosity by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.