Power law model viscosity
Home » Query » Power law model viscosityYour Power law model viscosity images are ready in this website. Power law model viscosity are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Power law model viscosity files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for power law model viscosity images information related to the power law model viscosity interest, you have come to the right site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Power Law Model Viscosity. The relation is given as. This behavior has been described by various models including the Bingham Plastic and Power Law models Bourgoyne et al 1986. For a Newtonian fluid n 1 and m is the viscosity. The power law material model can be used for all fluid flow analysis types.
 Pin On Useful Tips From pinterest.com
Pin On Useful Tips From pinterest.com
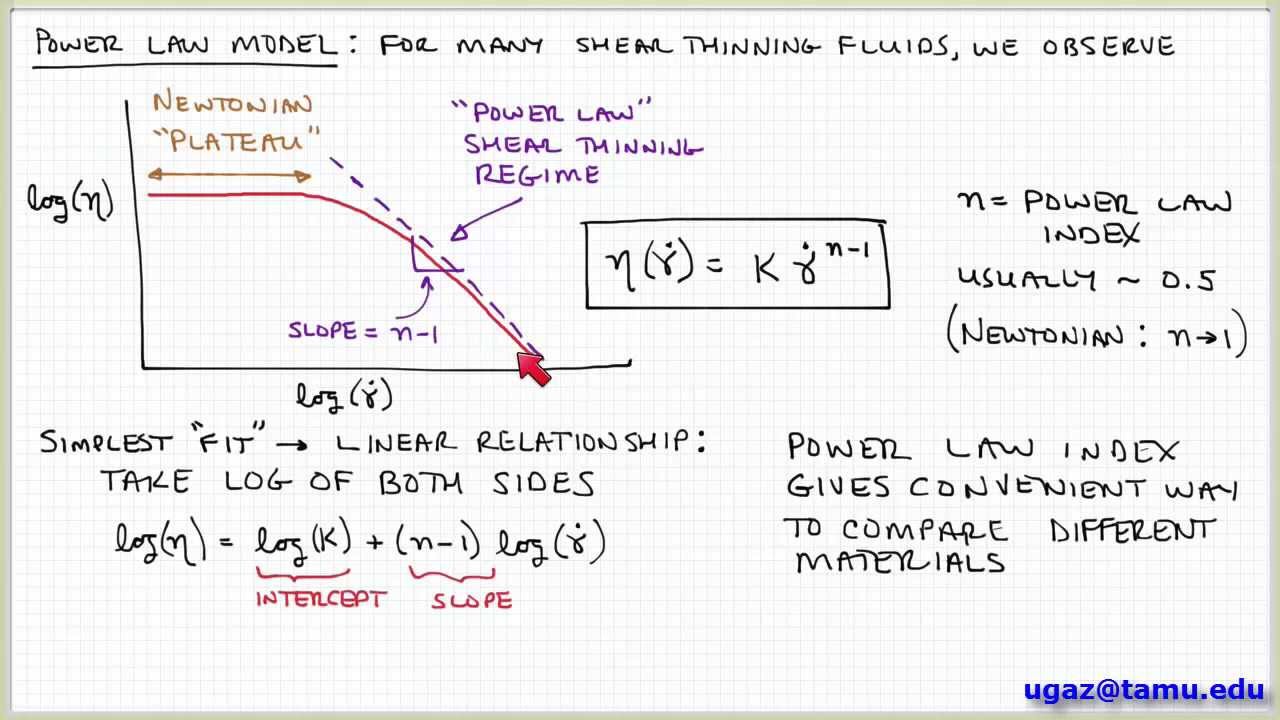
The Power law fluid model is a type of generalized model. Cross model is similar to Carreau model in that it is a four parameter model that covers the entire shear rate range Cross 1965. When being used for a steady or unsteady fluid flow analysis this material model will enforce maximum and minimum limits for the viscosity of the fluid based on the shear rates. The parameter m is known as the Cross Rate Constant. POWER-LAW m is called consistency index the larger the m the more viscous the melt n indicates the degree of Non-Newtonian behavior n1 means Newtonian n viscosity is a function of shear rate. η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau.
Halder 30 studied the stenosis shape effect on the resistance to arterial blood flow.
For a Newtonian fluid n 1 and m is the viscosity. Department of Physics Faculty of Science Tokyo Metropolitan University Setagaya Tokyo Japan. In a second step this averaged shear rate is used together with the rheology of the fluid to calculate. The parameter m is known as the Cross Rate Constant. Fluent has non newtonian power law viscosity model and you dont need to write a udf for itjust go to material and choose non newtonian powerlaw viscosity from viscosity tab and inter power law index n and K and 2 other parameters. This tells us how our product is likely to behave in very high shear processing situations such as blade knife and roller coating.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
η is the Infinite Shear Viscosity. These include the Bird-Carreau-Yasuda model the Cross-WLF model the Cross model and the Power-Law model. η is the Infinite Shear Viscosity. The power law material model can be used for all fluid flow analysis types. They found increasing velocity for rising magnetic flux current and density.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Department of Physics Faculty of Science Tokyo Metropolitan University Setagaya Tokyo Japan. The Power law model can be used to describe any material that shows power law behaviour. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds. In a second step this averaged shear rate is used together with the rheology of the fluid to calculate. The power law material model can be used for all fluid flow analysis types.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
K is often known as the consistency coefficient. Power-law equations are for high strain rates. For instance considering the area of a square in terms of the length of its side if the length is doubled the area is multiplied by a factor of four. The power-law fluid model is a 2. In statistics a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity independent of the initial size of those quantities.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The point on the viscosity versus shear rate curve where the flow changes from the lower Newtonian region to the Power law region. Department of Physics Faculty of Science Tokyo Metropolitan University Setagaya Tokyo Japan. Most popular model to express the shear-thinning behavior. These include the Bird-Carreau-Yasuda model the Cross-WLF model the Cross model and the Power-Law model. The Power law fluid model is a type of generalized model.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
N. It gives a basic relation for viscosity nu and the strain rate dotgamma. One simple model used to characterize non-Newtonian fluids is the power law model Macosko 1994. Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields. This tells us how our product is likely to behave in very high shear processing situations such as blade knife and roller coating.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It is dimensionless and is a measure of the degree of dependence of viscosity on shear rate in the shear-thinning region. The Power Law model is defined by where k is the power-law. When being used for a steady or unsteady fluid flow analysis this material model will enforce maximum and minimum limits for the viscosity of the fluid based on the shear rates. The parameter m is known as the Cross Rate Constant. They found increasing velocity for rising magnetic flux current and density.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
η is the viscosity mPa-s n is the power law constant unitless K is the flow consistency index mPa-s The power law model also known as the Ostwald de Waele relationship is used to fit non-Newtonian data across shear rates where there is no evidence of a Newtonian plateau. In statistics a power law is a functional relationship between two quantities where a relative change in one quantity results in a proportional relative change in the other quantity independent of the initial size of those quantities. One simple model used to characterize non-Newtonian fluids is the power law model Macosko 1994. The power law material model can be used for all fluid flow analysis types. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The model is nothing more than the Newtonian model with an added exponent on the shear rate term. Fluids that obey Newtons law of viscosity are called Newtonian fluids. One quantity varies as a power of another. Halder 30 studied the stenosis shape effect on the resistance to arterial blood flow. Explanation for the 34 power law of viscosity of polymeric liquids on the basis of the tube model.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
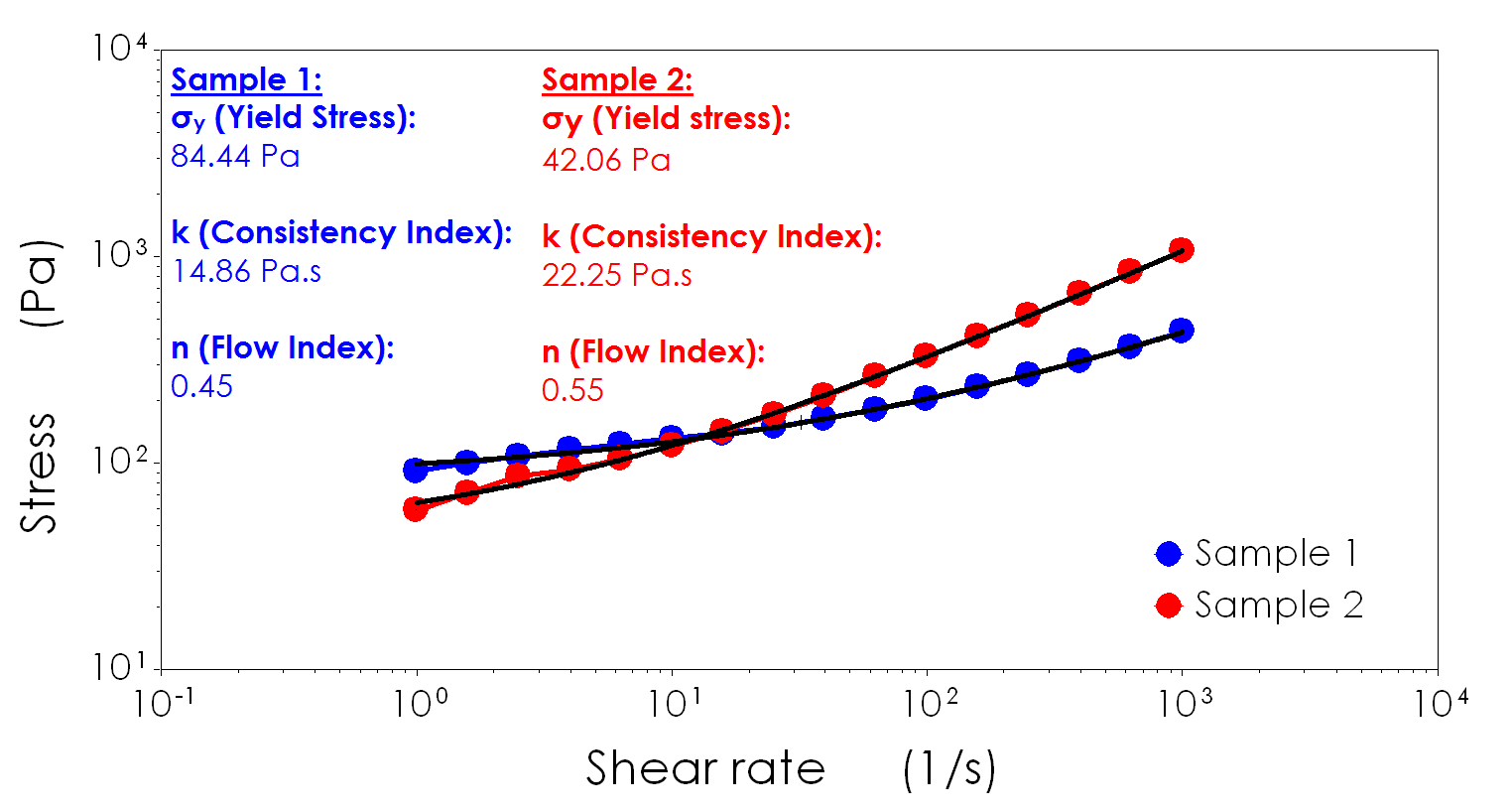
The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3. The Power law fluid model is a type of generalized model. Where n is Power-law index and k is consistency Pa-s. Explanation for the 34 power law of viscosity of polymeric liquids on the basis of the tube model. η min η η max.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Power-law fluids flowing in heterogeneous porous media is a natural nonlinear seepage flow phenomenon that has received much attention over the last three decades in an extensive variety of fields. These include the Bird-Carreau-Yasuda model the Cross-WLF model the Cross model and the Power-Law model. The model is nothing more than the Newtonian model with an added exponent on the shear rate term. M is the consistency and n is the power-law index. The power law model is commonly used to describe the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids.
 Source: rheologylab.com
Source: rheologylab.com
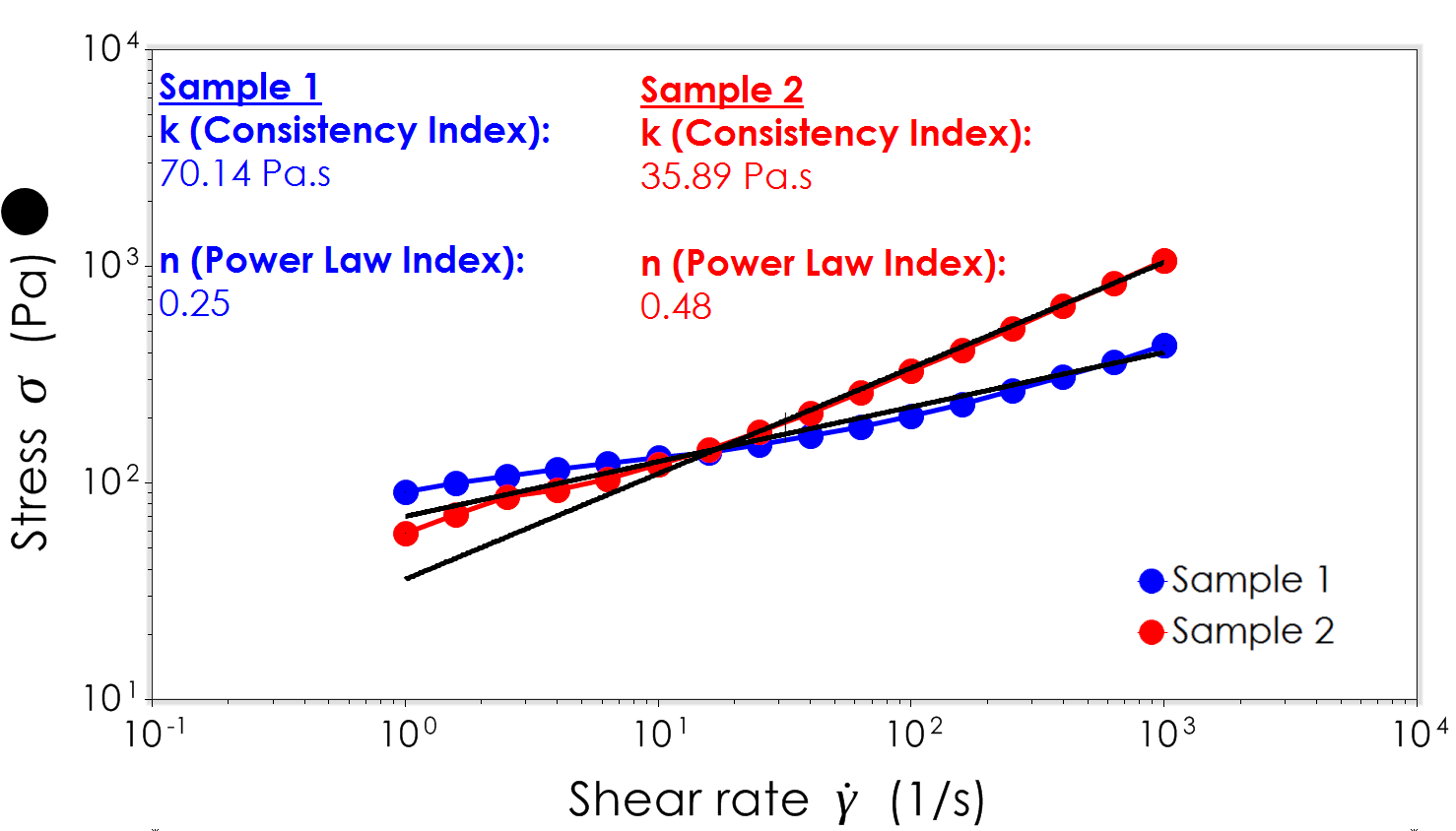
A power law index n1 denotes that the sample is shear thickening. Where n is Power-law index and k is consistency Pa-s. The power-law fluid model is a 2. The parameter m is known as the Cross Rate Constant. The point on the viscosity versus shear rate curve where the flow changes from the lower Newtonian region to the Power law region.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
1 Power law model. Originally Posted by raminostadi. Where n is Power-law index and k is consistency Pa-s. The parameter m is known as the Cross Rate Constant. They found increasing velocity for rising magnetic flux current and density.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
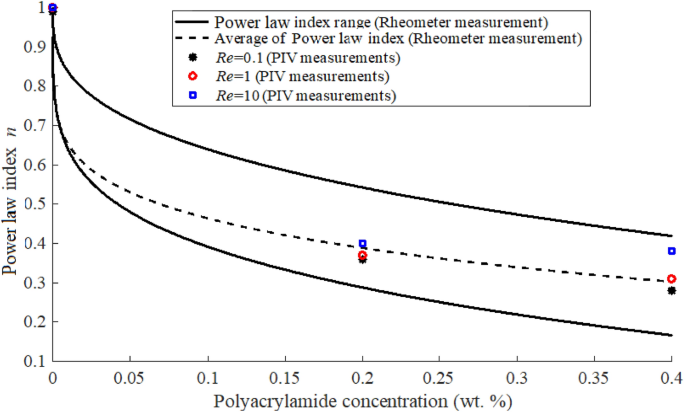
The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds. The power law and Casson Model were selected to calculate the viscosity power-law model is a simple consti-tutive model that shows good description of fluid behavior across the range of shear rates to which the coefficients were fitted while Casson model also considers yield stress in term of blood viscosity. Search for more papers by this author. The Power Law model and the Carreau model are most commonly used to describe the rheological behavior of the apparent viscosity decreasing as the shear rate increases shear thinning Green Willhite 1998. The Herschel-Bulkley HB viscosity model also called Yield Power Law YPL model is known to correlate better to the drilling fluid viscosity curve than most other rheological models 2 3.
 Source: rheologylab.com
Source: rheologylab.com
N. Search for more papers by this author. Typical values for n are given in appendix A and range from about 02 to close to 1. The power law model is commonly used to describe the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids. Department of Physics Faculty of Science Tokyo Metropolitan University Setagaya Tokyo Japan.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
K is often known as the consistency coefficient. This parameters depend on material properties. The relation is given as. For instance considering the area of a square in terms of the length of its side if the length is doubled the area is multiplied by a factor of four. The friction factor is correlated against the power-law Reynolds.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
These include the Bird-Carreau-Yasuda model the Cross-WLF model the Cross model and the Power-Law model. In a second step this averaged shear rate is used together with the rheology of the fluid to calculate. η min η η max. In this model the value of viscosity can be bounded by a lower bound value nu_min and an upper bound value nu_max. The Power law model can be used to describe any material that shows power law behaviour.

When being used for a steady or unsteady fluid flow analysis this material model will enforce maximum and minimum limits for the viscosity of the fluid based on the shear rates. This tells us how our product is likely to behave in very high shear processing situations such as blade knife and roller coating. 1 Power law model. It is dimensionless and is a measure of the degree of dependence of viscosity on shear rate in the shear-thinning region. One quantity varies as a power of another.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In literature most experimental studies on drilling fluids observed that the drilling fluid rheological curves rheogram conformed best to that of YPL. In a second step this averaged shear rate is used together with the rheology of the fluid to calculate. 1 Power law model. The point on the viscosity versus shear rate curve where the flow changes from the lower Newtonian region to the Power law region. Most popular model to express the shear-thinning behavior.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title power law model viscosity by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.