Lithium halogen exchange mechanism
Home » Query » Lithium halogen exchange mechanismYour Lithium halogen exchange mechanism images are ready. Lithium halogen exchange mechanism are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Lithium halogen exchange mechanism files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for lithium halogen exchange mechanism images information connected with to the lithium halogen exchange mechanism keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Lithium Halogen Exchange Mechanism. The lithium trialkyl magnesiates are prepared in situ by the addition of an alkyl lithium 2 equiv to an alkyl magnesium halide 1 equiv. Very recently the Alexakis group achieved the catalytic brominelithium exchange allowing the preparation of biarylatropisomers in quantitative yields and enantiomeric excesses up to 82. Organolithiums via LithiumHalogen Exchange. This is correct - it is an equilibrium reaction.
 The Metal Halogen Exchange Interaction Of Phenyllithium With Iodobenzene From www2.chem.wisc.edu
The Metal Halogen Exchange Interaction Of Phenyllithium With Iodobenzene From www2.chem.wisc.edu
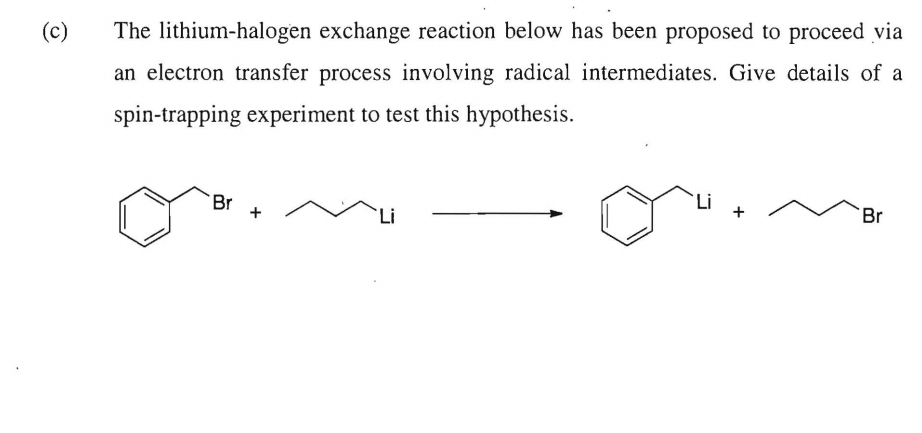
Lithium-halogen exchange reactions proceed in the direction of forming the more stable organolithium reagent that is the one derived from the more acidic compound by using the more basic organolithium compounds such as n-BuLi and t-BuLi. Preliminary studies of the mechanism of metal-halogen exchange. Organolithium reagents are themselves produced for example by halogen-metal exchange lithiation of organic halides or. Magnesiates exhibit a reactivity somewhere between alkyllithium and alkylmagnesium reagents. Herein we report on the preparation of C 1 analogues of the most efficient and popular C 2-symmetric biphenyl ligands. The mechanism of the lithium - halogen Interchange reaction.
You might reason that the products could react backwards using the same principles.
Interestingly when ceR aryl particularly bromides and iodides this is best written as ceRLi RX RLi RX. Organolithiums via LithiumHalogen Exchange. Metalation and Halogen-Lithium Exchange of Sensitive Substrates and Mild Ester Homologation in Continuous Flow von Maximilian Andreas Ganiek aus Augsburg 2018. Theoretical studies on the mechanism of halogen-lithium exchange in PhBr were carried out earlier by Ando. The exchange reaction is faster and less sensitive to electronic effects arene substitution. Example Example Retention of configuration is often observed when organolithium compounds are.
Source:
28 In those studies MeLi was used as the model lithiating agent. Lithium-halogen exchange reaction from occuring between the cyclopropyllithium reagent and the aryl iodide. The kinetics of reaction of n-butyllithium with substituted bromobenzenes in hexane solution. Shows that the mechanism for which lithiumhalogen exchange occurs through the formation of the ate-complex when a Lewis acid combines with a Lewis base whereby the central atom from the Lewis acid increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge as proposed in the literature. The mechanism of the lithium - halogen Interchange reaction.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Metalation and Halogen-Lithium Exchange of Sensitive Substrates and Mild Ester Homologation in Continuous Flow von Maximilian Andreas Ganiek aus Augsburg 2018. This is correct - it is an equilibrium reaction. Organolithium reagents are used for lithium-halogen exchange ortho metalation and to produce other nucleophilic organometallics such as boron reagents. Reaction proceeds in forward direction when new RLi formed is a weaker base more stable carbanion than the starting RLi. Shows that the mechanism for which lithiumhalogen exchange occurs through the formation of the ate-complex when a Lewis acid combines with a Lewis base whereby the central atom from the Lewis acid increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge as proposed in the literature.

Organolithiums via LithiumHalogen Exchange. The exchange reaction is faster and less sensitive to electronic effects arene substitution. The most applicable method involves SnLi exchange Scheme 1 eq. Lithium-halogen exchange reactions proceed in the direction of forming the more stable organolithium reagent that is the one derived from the more acidic compound by using the more basic organolithium compounds such as n-BuLi and t-BuLi. Today this reversible lithium-halogen exchange reaction can be formulated as ceRLi RX K RLi RX As an equilibrium process we know that the more stable lithium species is preferred.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Preliminary studies of the mechanism of metal-halogen exchange. Today this reversible lithium-halogen exchange reaction can be formulated as ceRLi RX K RLi RX As an equilibrium process we know that the more stable lithium species is preferred. ERKLÄRUNG Diese Dissertation wurde im Sinne von 7 der Promotionsordnung vom 28. The most applicable method involves SnLi exchange Scheme 1 eq. Theoretical studies on the mechanism of halogen-lithium exchange in PhBr were carried out earlier by Ando.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Today this reversible lithium-halogen exchange reaction can be formulated as ceRLi RX K RLi RX As an equilibrium process we know that the more stable lithium species is preferred. Interestingly when ceR aryl particularly bromides and iodides this is best written as ceRLi RX RLi RX. In these situations the lithiummetalloid exchange reactions may provide the best route3 RM n-BuLi 6 R-Li n-BuM The LiBr LiI LiSn and LiSe are the transmetalations most commonly used. Organolithiums via LithiumHalogen Exchange. The mechanism of the lithium - halogen Interchange reaction.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Consider the relative rates of the processes that must occur in the above transformation. This is correct - it is an equilibrium reaction. The LiM exchanges are extremely fast especially LiI LiHg and LiTe and have been used to prepare unstable lithium reagents at very low. Today this reversible lithium-halogen exchange reaction can be formulated as ceRLi RX K RLi RX As an equilibrium process we know that the more stable lithium species is preferred. For heterocycles alkyl lithium bases are used as well as lithium amides.
 Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
Performed by Gilman determined lithiumhalogen exchange to be an equilibrium process favoring the formation of the less basic more stable organolithium2 Transmetalation occurs 35 through formation of a lithium-metal ate complex followed by lithium-metal exchange3. Today this reversible lithium-halogen exchange reaction can be formulated as ceRLi RX K RLi RX As an equilibrium process we know that the more stable lithium species is preferred. The kinetics of reaction of n-butyllithium with substituted bromobenzenes in hexane solution. We will show that by means of regioselective brominelithium exchanges all possible. You might reason that the products could react backwards using the same principles.
 Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
Consider the relative rates of the processes that must occur in the above transformation. The exchange reaction is faster and less sensitive to electronic effects arene substitution. Herein we report on the preparation of C 1 analogues of the most efficient and popular C 2-symmetric biphenyl ligands. You might reason that the products could react backwards using the same principles. The most applicable method involves SnLi exchange Scheme 1 eq.
 Source: wiki2.org
Source: wiki2.org
For heterocycles alkyl lithium bases are used as well as lithium amides. The kinetics of reaction of n-butyllithium with substituted bromobenzenes in hexane solution. Subsequent studies of the reactions of PhLi with fluorobenzene led to the first example of a reaction proceeding via a benzyne intermediate Wittig G. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 1988 352. Magnesiates exhibit a reactivity somewhere between alkyllithium and alkylmagnesium reagents.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Solvent choices for these lithiations are usually ether or THF. A possible mechanism for the reaction is shown in scheme 7. Shows that the mechanism for which lithiumhalogen exchange occurs through the formation of the ate-complex when a Lewis acid combines with a Lewis base whereby the central atom from the Lewis acid increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge as proposed in the literature. N Cl O H Br O O H3C CH3 OH TBSO N Cl O O O. Theoretical studies on the mechanism of halogen-lithium exchange in PhBr were carried out earlier by Ando.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
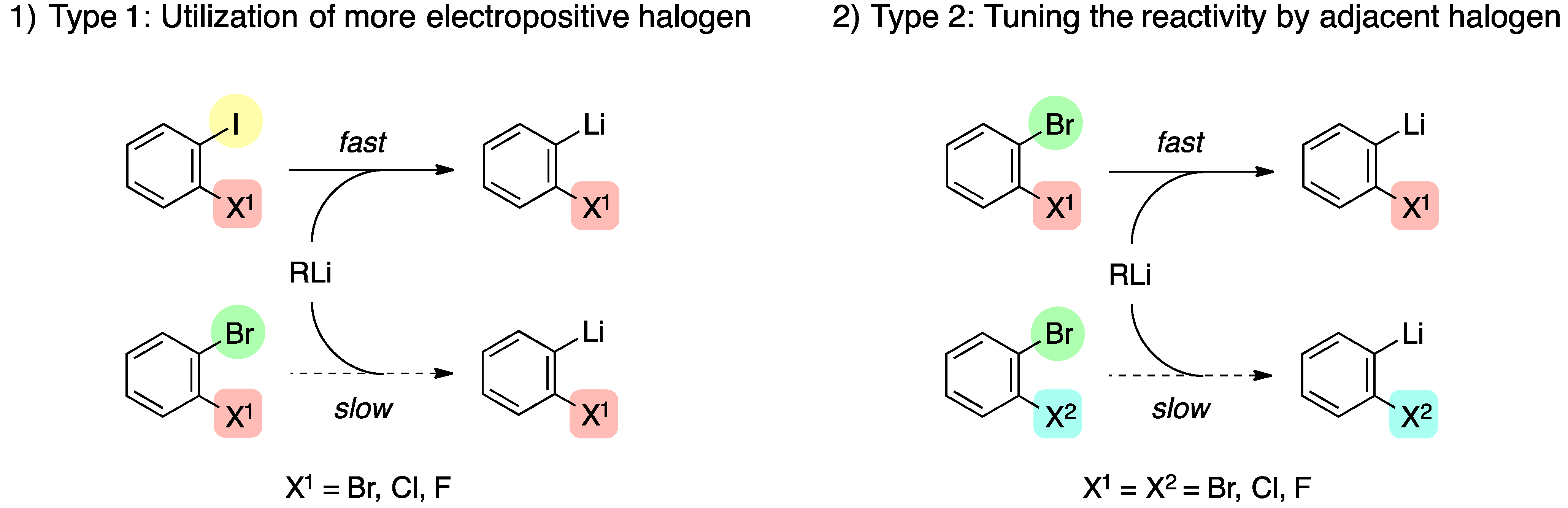
Here it is proposed that the halogen-lithium exchange reaction occurs first before the hydrogen at N-lithium exchange to give 7. Consider the relative rates of the processes that must occur in the above transformation. Subsequent studies of the reactions of PhLi with fluorobenzene led to the first example of a reaction proceeding via a benzyne intermediate Wittig G. Lithium-halogen exchange reactions proceed in the direction of forming the more stable organolithium reagent that is the one derived from the more acidic compound by using the more basic organolithium compounds such as n-BuLi and t-BuLi. HO SO2Ph 22 eq n-BuLi THF 78 C OCH3 O OH SO2Ph OH O OH N H3C 60 Morphine Toth J.
 Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
Source: www2.chem.wisc.edu
We will show that by means of regioselective brominelithium exchanges all possible. HO SO2Ph 22 eq n-BuLi THF 78 C OCH3 O OH SO2Ph OH O OH N H3C 60 Morphine Toth J. The lithium trialkyl magnesiates are prepared in situ by the addition of an alkyl lithium 2 equiv to an alkyl magnesium halide 1 equiv. Example Example Retention of configuration is often observed when organolithium compounds are. Lithium-halogen exchange reaction from occuring between the cyclopropyllithium reagent and the aryl iodide.
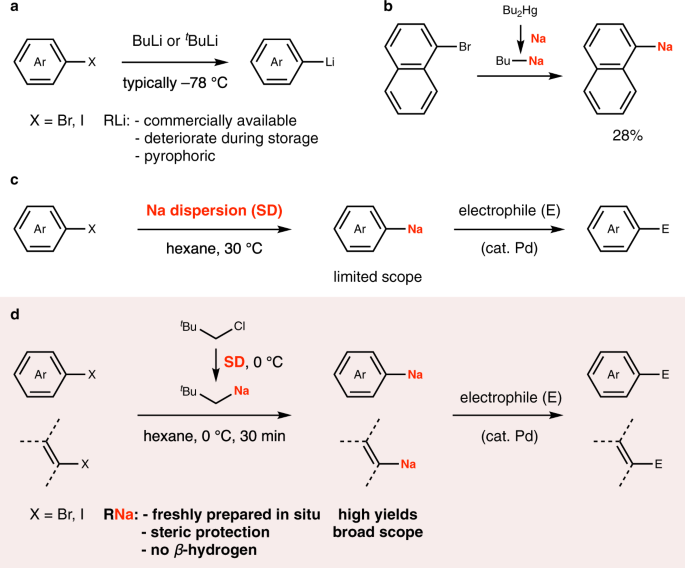 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Shows that the mechanism for which lithiumhalogen exchange occurs through the formation of the ate-complex when a Lewis acid combines with a Lewis base whereby the central atom from the Lewis acid increases its valence and gains a negative formal charge as proposed in the literature. In general lithium-halogen exchange can occur either via a polar mechanism such as the one shown above or via a radical mechanism by two successive electron transfers from RLi to RX. HO SO2Ph 22 eq n-BuLi THF 78 C OCH3 O OH SO2Ph OH O OH N H3C 60 Morphine Toth J. Interestingly when ceR aryl particularly bromides and iodides this is best written as ceRLi RX RLi RX. The First LithiumHalogen Exchange Reaction In 1938 Wittig is surprised by his discovery of lithiumhalogen interconversion.
Source:
A possible mechanism for the reaction is shown in scheme 7. The most applicable method involves SnLi exchange Scheme 1 eq. The First LithiumHalogen Exchange Reaction In 1938 Wittig is surprised by his discovery of lithiumhalogen interconversion. For heterocycles alkyl lithium bases are used as well as lithium amides. However lithium-halogen exchange can provide the 2-lithiated pyridine Things to consider.
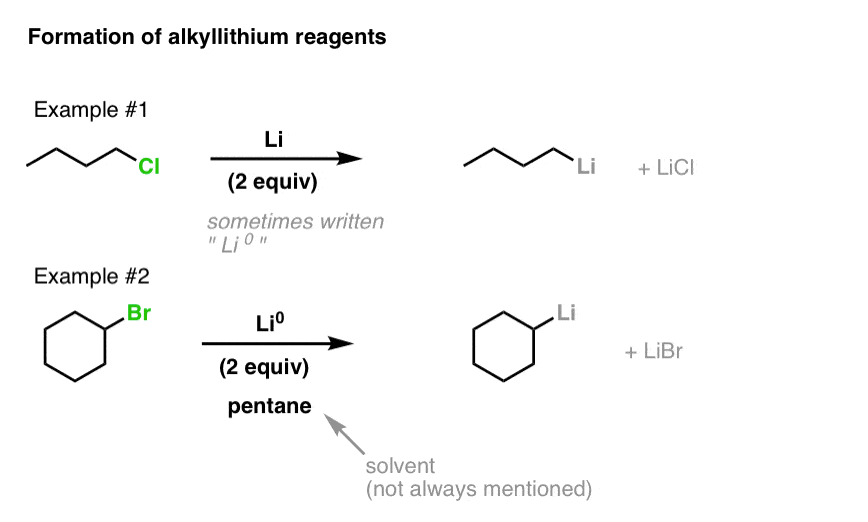 Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Source: masterorganicchemistry.com
Very recently the Alexakis group achieved the catalytic brominelithium exchange allowing the preparation of biarylatropisomers in quantitative yields and enantiomeric excesses up to 82. Example Example Retention of configuration is often observed when organolithium compounds are. Reaction proceeds in forward direction when new RLi formed is a weaker base more stable carbanion than the starting RLi. Lithium-halogen exchange reaction from occuring between the cyclopropyllithium reagent and the aryl iodide. Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 1988 352.
Source:
A review of the literature. The lithium trialkyl magnesiates are prepared in situ by the addition of an alkyl lithium 2 equiv to an alkyl magnesium halide 1 equiv. The kinetics of reaction of n-butyllithium with substituted bromobenzenes in hexane solution. Method is best suited for exchanges between Csp3Li stronger base and Csp2X to give alkenyllithiums Csp Li weaker base. In general lithium-halogen exchange can occur either via a polar mechanism such as the one shown above or via a radical mechanism by two successive electron transfers from RLi to RX.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In addition to the heteroatom DMGs will influence the metalation site. The mechanism of the lithium - halogen Interchange reaction. For heterocycles alkyl lithium bases are used as well as lithium amides. Here it is proposed that the halogen-lithium exchange reaction occurs first before the hydrogen at N-lithium exchange to give 7. Organolithium reagents are used for lithium-halogen exchange ortho metalation and to produce other nucleophilic organometallics such as boron reagents.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
N Cl O H Br O O H3C CH3 OH TBSO N Cl O O O. Interestingly when ceR aryl particularly bromides and iodides this is best written as ceRLi RX RLi RX. The First LithiumHalogen Exchange Reaction In 1938 Wittig is surprised by his discovery of lithiumhalogen interconversion. Example Example Retention of configuration is often observed when organolithium compounds are. A review of the literature.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title lithium halogen exchange mechanism by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.